Explore the essentials of balancing machines
This article will discuss balancing machines, their types, design features, working principles, and help you choose the right machine.
2. Purpose and Application
A balancing machine is a technological device designed to eliminate static or dynamic unbalance in rotating parts (rotors). Imbalance can lead to vibration, increased wear, and equipment failures.
Balancing machines are used in various industries, including:
- Mechanical engineering: balancing shafts, pulleys, gears, couplings, and other parts
- Aviation: balancing turbines, engine rotors, propellers, and other elements
- Automotive industry: balancing wheels, driveshafts, brake discs
- Energy: balancing turbine rotors, generators, pumps
3. Types of Balancing Machines
There are two main types of balancing machines:
3.1 Resonance Machines
Advantages:
- Simple design: Resonance machines have a relatively simple construction, making them more affordable and easier to maintain.
- Low cost: As a consequence of their simplicity, resonance machines are usually less expensive.
- High sensitivity to imbalance: Thanks to flexible supports, resonance machines can detect even minor deviations in balance.
- They provide good quality balancing for light rotors (up to 200 kg): Resonance machines are suitable for balancing small rotors such as pulleys, couplings, drive components.

Disadvantages:
- Limited by load capacity: Resonance machines are not suitable for balancing heavy rotors (over 200 kg).
- Not suitable for balancing rotors at critical rotation frequencies: At critical frequencies, resonance vibrations of the supports can distort the balancing results.

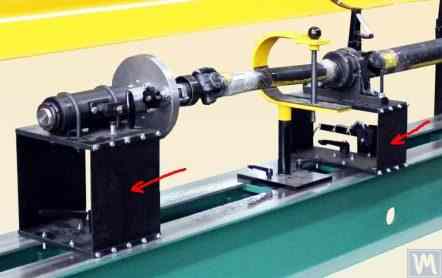
3.2 Pre-resonance Machines
Advantages:
- Versatility: Pre-resonance machines are suitable for balancing rotors of various masses and dimensions, both light and heavy.
- Ability to balance at low rotation frequencies: This allows rotors to be balanced at operating speeds, which improves the accuracy of the balancing.
- High precision: Pre-resonance machines provide higher precision balancing compared to resonance machines.
Disadvantages:
- More complex construction: Pre-resonance machines have a more complex construction than resonance machines, which leads to higher costs.
- Higher cost: As a result of the complexity, pre-resonance machines are more expensive.

4. Design Features
4.1 Resonance Machines
Supports: Resonance machines have flexible supports, made from spring suspensions, spring-loaded carriages, flat or cylindrical spring supports.
Sensors: Vibration sensors are used to measure rotor vibration.
Control System: The machine's control system analyzes data from the sensors and calculates the parameters of the correcting weights needed to eliminate imbalance.
4.2 Pre-resonance Machines
Supports: Pre-resonance machines have rigid supports, made in the form of plates with figured slots.
Sensors: Force sensors or highly sensitive vibration sensors are used to measure the deformation of the supports.
Control System: The machine's control system analyzes data from the sensors and calculates the parameters of the correcting weights needed to eliminate imbalance.
5. Choosing a Balancing Machine
The choice of a balancing machine depends on the following factors:
- Type of rotor:
- Mass and dimensions: This determines the load capacity and size of the working space of the machine.
- Operating rotation frequency: The critical frequencies of the rotor should be outside the operating range of the resonance machine.
- Type of bearings: The rotor bearings affect the transmission of vibration to the machine's supports.
- Required precision of balancing: High-precision components need pre-resonance machines with precision sensors. Resonance machines may be sufficient for less strict requirements.
- Productivity: If you are balancing many parts, consider a machine with automatic loading/unloading and quick setup features.
- Budget: Resonance machines are economically more advantageous, but pre-resonance machines are more versatile and accurate. Assess long-term needs and return on investment.
6. Recommendations for Selection
For balancing light rotors (up to 200 kg) in conditions of a limited budget, resonance machines are suitable.
For balancing rotors of various masses and dimensions, as well as for high-precision balancing, pre-resonance machines are recommended.
When choosing a machine, it is important to:
- Read reviews from other users
- Compare the technical specifications of different models
- Consult with equipment suppliers to select the optimal balancing machine
7. Conclusion
Balancing machines are an essential tool for ensuring reliable and long-lasting operation of rotating parts. A careful selection of a balancing machine, considering your needs and budget, will help you improve the quality of your products, reduce equipment downtime, and lower operating costs.
8. Note
This article is only a brief overview of DIY balancing machines: https://vibromera.eu/diy-balancing-machines/ For specialized applications or large-scale production, consultation with a balancing equipment expert may be required.