The S-8880A Series developed by SII Semiconductor is a boost charge pump for step-up DC-DC converter startup, which enables operation with ultra-low power and ultra-low voltage. An original circuit system and SOI technology allow this product to boost the industry’s lowest level 0.35 V ultra-low input voltage as a boost charge pump, and achieve operation with an extremely weak power of 26 μW.
The boosted electric power is stored in an external startup capacitor, and it is discharged as the startup power of the step-up DC-DC converter when the startup capacitor reaches the discharge start voltage (VCPOUT1). A built-in power-off function is also provided, so that when the output voltage of the connected step-up DC-DC converter rises above a given value, the operation is stopped, thereby achieving significant power saving and contributing to lower power consumption of devices.
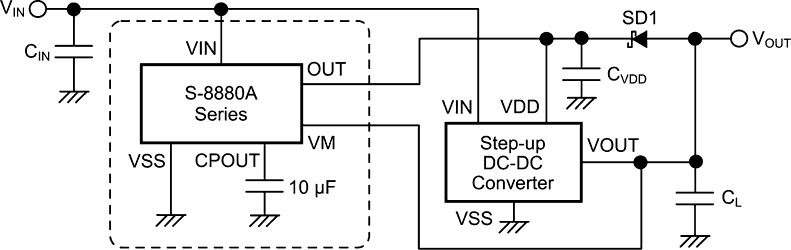 |
| Typical Application Circuit. |
It also includes boost flying capacitors, which allows for formation of a step-up DC-DC converter startup circuit by adding a minimum of just one external capacitor, thus realizing miniaturization of devices.
Features
- Ultra-low power and ultra-low voltage operation: Input power at startup (PIN(START-UP)) = 26 μW typ. (VCPOUT1(S) = 1.8 V, VIN = 0.35 V) (Ta = +25°C)
- Minimum operation input voltage
- 0.35 V (VCPOUT1(S) = 1.8 V) (Ta = +25°C)
- 0.39 V (VCPOUT1(S) = 1.8 V to 2.4 V) (Ta = −40 °C to +85 °C)
- Current consumption during operation: 74 μA typ. (VIN = 0.35 V)
- Discharge start voltage: VCPOUT1(S) = 1.8 V to 2.4 V (Selectable in 0.2 V step)
- Power-off voltage: VCPOUT1 + 0.1 V (Fixed internally)
- External component: Startup capacitor (CCPOUT) × 1 unit
- Operation temperature range: Ta = −40 °C to +85°C
- Lead-free (Sn 100%), halogen-free
Applications
- Boosting from low-voltage power supply
- Boosting internal power supply voltage of RF tag
- Intermittently power supplying to intermittent operation system
- Energy harvesting
