Space-saving LFPAK56D half-bridge offers 60% lower parasitic inductance and improved thermal performance for power train, motor control and DC/DC application
Nexperia announced a series of half-bridge (high side & low side) automotive MOSFETs constructed in the space-saving LFPAK56D package format. The half-bridge configuration of two MOSFETs is a standard building block for many automotive applications including motor drives and DC/DC converters. The new package provides a half-bridge solution in one device, occupying 30% lower PCB area compared to dual MOSFETs for 3-phase motor control topologies due to the removal of PCB tracks, whilst permitting simple automated optical inspection (AOI) during production. The LFPAK56D half-bridge utilises existing high volume LFPAK56D assembly processes with proven automotive reliability. The package format uses flexible leads to improve overall reliability, and an internal copper clip connection between the MOSFETs simplifies PCB designs and brings a plug and play style solution with exceptional current handling capability of 98 A.
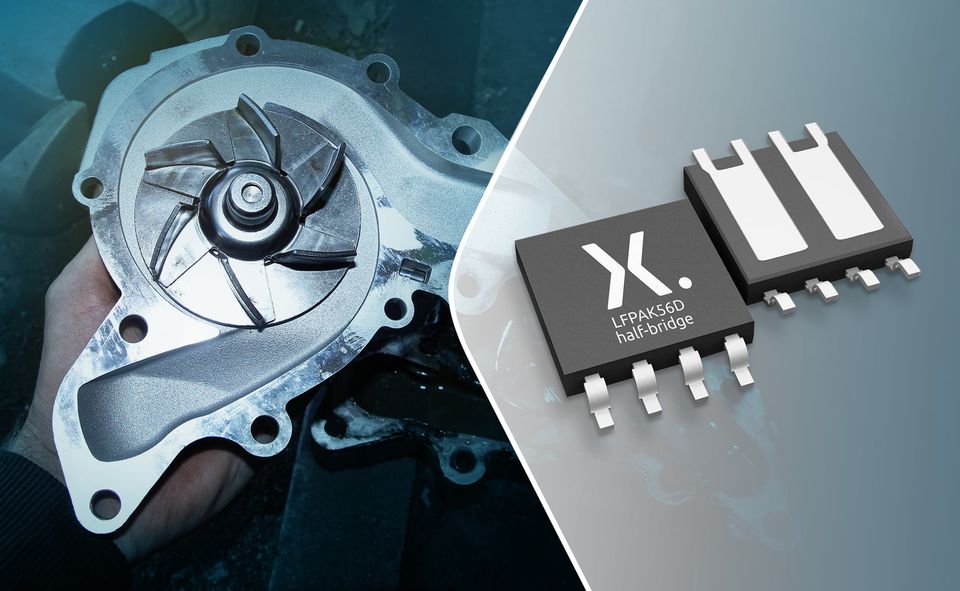
Typically, in a half-bridge arrangement, the PCB connection between the source of the high side MOSFET and the drain of the low side MOSFET can create a significant amount of parasitic inductance. However, with its internal clip connection, the LFPAK56D half-bridge package achieves 60% less inductance.
The new LFPAK56D half-bridge MOSFETs launched are the BUK7V4R2-40H and the BUK9V13-40H. Both utilise the highly robust Trench 9 automotive silicon process technology, are rated at 40 V and are verified at twice the automotive AEC-Q101 specification in key tests. RDS(on) of the devices measures 4.2 mOhm (BUK7V4R2) and 13 mOhm (BUK9V13).
The AEC-Q101-qualified Nexperia LFPAK56D half-bridge package suits a broad range of 3-phase automotive powertrain applications such as fuel and water pumps, motor control and DC/DC power conversion, occupying 30% lower PCB area and 60% lower parasitic inductance for high performance switching applications. The new technology has already seen success with design-in and commitment from major automotive customers.
