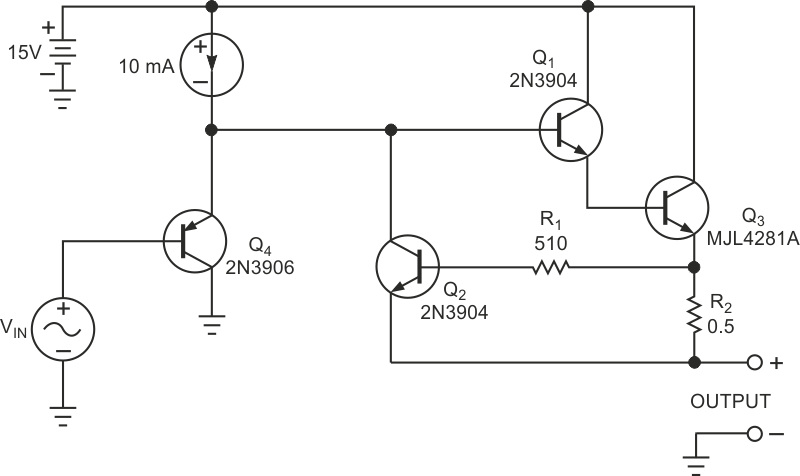
Adding current-limiting circuitry to a power amplifier's or a linear voltage regulator's emitter-follower output stage protects both the output transistor and the downstream circuitry from excessive-current damage. Figure 1 shows the classic current-limiter circuit: Transistor Q2 senses the output-current-induced voltage drop across ballast resistor R2 and diverts base current from Darlington-connected transistors Q1 and Q3. Transistor Q2's base-emitter voltage, VBE, sets the circuit's current-limit threshold. Unfortunately, a small-signal transistor's VBE exhibits a temperature coefficient of –2 mV/°C, which causes a substantial variation in the current-limiting threshold over the circuit's operating-temperature range.
 |
||
| Figure 1. | A small-signal transistor, Q2, provides an output-current limit for this emitter-follower power amplifier. |
|
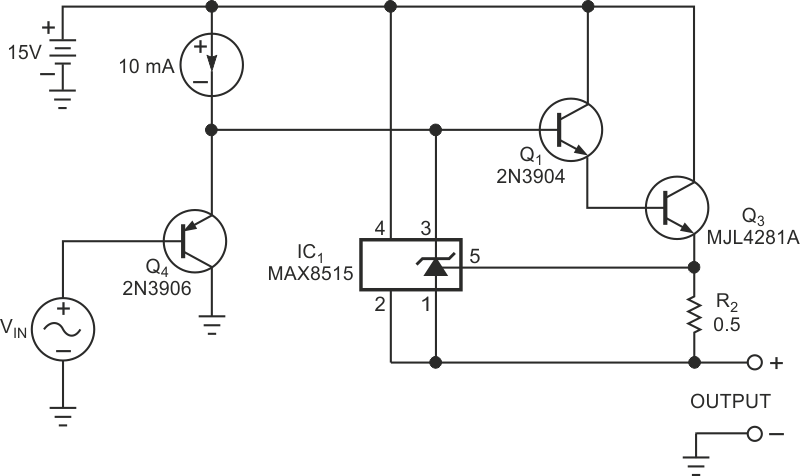
You can improve the circuit's performance by replacing Q2 with IC1, an adjustable shunt regulator (Figure 2). With an input threshold voltage of 0.6 V, the MAX8515 allows use of a lower value for current-sense resistor R2 and thus helps minimize R2's power and thermal losses. Alternative commonly available shunt regulators present input voltages of 1.25 to 2.5 V. In addition, a separate power-supply input connection allows the MAX8515 to maintain accuracy when its internal output transistor approaches saturation.
 |
||
| Figure 2. | Substituting a shunt regulator, IC1, for Q2 in Figure 1 improves the output-current-limit accuracy. |
|
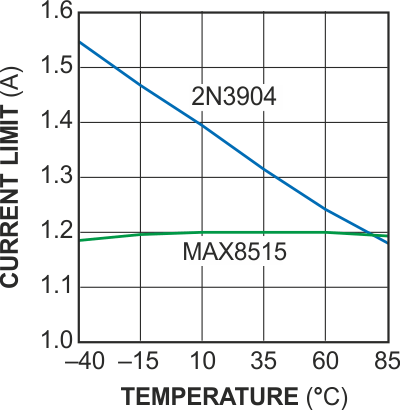
Figure 3 compares current-limit accuracy for the circuits of Figure 1 and Figure 2 over an operating-temperature range of –40 to +85 °C. Neglecting the temperature coefficient of sense resistor R2, the shunt-regulator version maintains its output current to an accuracy of better than 2%, and the small-signal-transistor version exhibits a 25% current variation over the operating-temperature range.
 |
||
| Figure 3. | Output-current-versus-temperature plots for the circuits of figures 1 and 2 show improved accuracy for the shunt-regulated circuit (bottom trace) over the discrete-transistor version (top trace). |
|
