Microchip Technology offers a family of cooling-fan speed controllers that operate in PWM mode for use with brushless dc fans (
Reference 1). To control fan speed using the PWM waveform's duty cycle, you can use either an external NTC (negative-temperature-coefficient) thermistor or one of Microchip's PIC microcontrollers and its SMBus serial-data bus. Figure 1 illustrates a typical application that the data sheet describes for the TC664 and TC665 controllers (
Reference 2). Using a frequency-control capacitor, CF, with a value of 1 µF, fan-controller IC1 generates a PWM pulse train with a nominal frequency of 30 Hz and a temperature- or command-dependent duty cycle that varies from 30 to 100%.
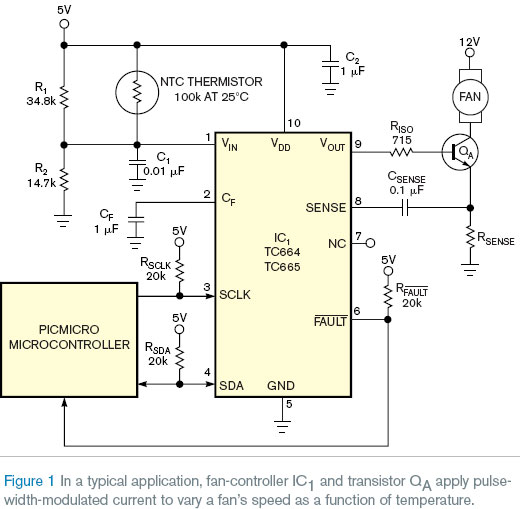
Although using the controller in PWM mode reduces power dissipation in transistor QA, which drives the fan, the 100-mA, square-wave motor-drive current can cause unwanted interference in a nearby high-sensitivity audio circuit. The circuit in Figure 2 solves the problem. An additional driver transistor, Q1, and an RC network comprising C3 and R3 form a simple PWM-to-linear converter. You can also use another PWM-to-linear-conversion circuit, such as an integrator based on an operational amplifier.
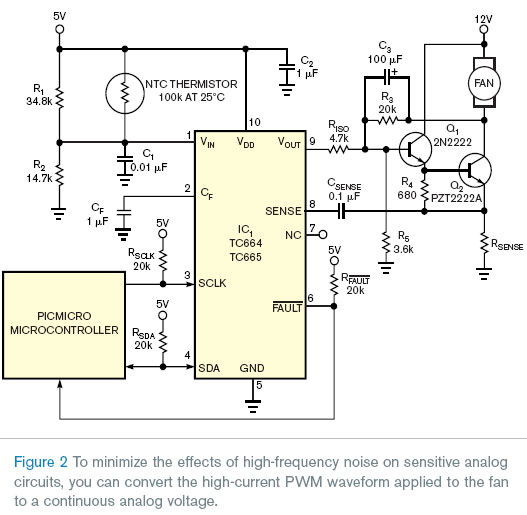
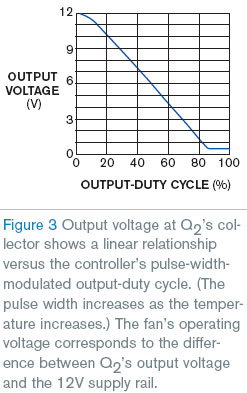
Figure 3 shows a graph of the dc voltage at Q2's collector versus IC1's PWM drive-output waveform's duty cycle. The voltage applied to the fan corresponds to the difference between Q2's collector voltage and the 12 V supply voltage. Even though a steady voltage appears across the fan, current pulses that the fan motor's commutation produces still develop a voltage across current-sense resistor RSENSE that connect to Q2's emitter, and all of IC1's protective and advisory features remain available.
The listed component values are valid for a 100-mA, 12 V, brushless fan. Use a general-purpose NPN transistor such as the 2N2222 for driver-transistor Q1 and an NPN transistor, such as Fairchild Semiconductor's PZT2222A, that can dissipate one-third of the fan's maximum power consumption for Q2. Note that you can vary the PWM's nominal frequency over a range of 15 to 35 Hz by altering the value of CF.





