- Flashes a LED when detecting an incoming call
- Powered by one 1.5V cell
Circuit diagram:
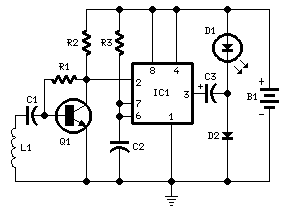
|
Parts: |
|
|
R1 |
100K 1/4W Resistor |
|
R2 |
3K9 1/4W Resistor |
|
R3 |
1M 1/4W Resistor |
|
C1, C2 |
100nF 63V Polyester Capacitors |
|
C3 |
220µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor |
|
D1 |
LED Red 10mm. Ultra-bright (see Notes) |
|
D2 |
1N5819 40V 1A Schottky-barrier Diode (see Notes) |
|
Q1 |
BC547 45V 100mA NPN Transistor |
|
IC1 |
7555 or TS555CN CMOS Timer IC |
|
L1 |
Sensor coil (see Notes) |
|
B1 |
1.5V Battery (AA or AAA cell etc.) |
Device purpose:
This circuit was designed to detect when a call is incoming in a cellular phone (even when the calling tone of the device is switched-off) by means of a flashing LED.
The device must be placed a few centimeters from the cellular phone, so its sensor coil L1 can detect the field emitted by the phone receiver during an incoming call.
Circuit operation:
The signal detected by the sensor coil is amplified by transistor Q1 and drives the monostable input pin of IC1. The IC's output voltage is doubled by C2 & D2 in order to drive the high-efficiency ultra-bright LED at a suitable peak-voltage.
Notes:
- Stand-by current drawing is less than 200µA, therefore a power on/off switch is unnecessary.
- Sensitivity of this circuit depends on the sensor coil type.
- L1 can be made by winding 130 to 150 turns of 0.2 mm. enameled wire on a 5 cm. diameter former (e.g. a can). Remove the coil from the former and wind it with insulating tape, thus obtaining a stand-alone coil.
- A commercial 10mH miniature inductor, usually sold in the form of a tiny rectangular plastic box, can be used satisfactorily but with lower sensitivity.
- IC1 must be a CMOS type: only these devices can safely operate at 1.5V supply or less.
- Any Schottky-barrier type diode can be used in place of the 1N5819: the BAT46 type is a very good choice.
