EDN
IR (infrared)-proximity sensors can sense the presence of an object, its distance from a reference, or both. Applications include speed detection, sensing of the hand in automatic faucets, automatic counting or detection of objects on conveyer belts, and paper-edge detection in printers. The latest-generation smartphones, for example, can turn off the LCD touchscreen to prevent the accidental activation of buttons when you press the screen against your chin or your ear.
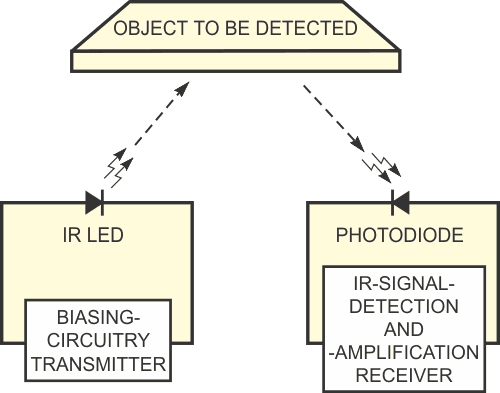
To sense an object, a proximity sensor transmits IR pulses toward the object and then “listens” to detect any pulses that reflect back. An IR LED transmits the IR signals, and an IR photodetector detects the reflected signal (Figure 1). The strength of this reflected signal is inversely proportional to the distance of the object from the IR transceiver. Because the reflected IR signal is stronger when the object is close, you can calibrate the output of the photodiode detector to determine the exact trigger distance of an object. The trigger distance indicates the threshold for making a decision on whether an object is present.
 |
||
| Figure 1. | An IR-proximity sensor detects an object by receiving reflected light. | |
The photodiode detects IR not only that the object reflects, but also from the ambient conditions. You must filter out this IR noise to prevent false detections. A common method is to modulate the LED's IR signal with a convenient frequency and then detect only the IR with that modulation, which identifies it as a reflection from the object.
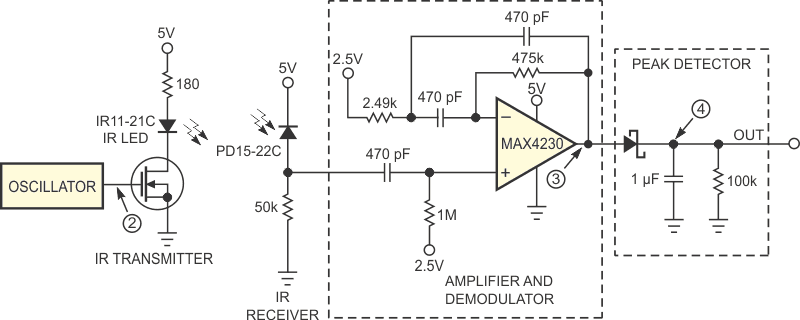
This Design Idea describes an IR-proximity sensor with simple transmitter and receiver sections (Figure 2). The transmitter consists of an Everlight 940-nm IR11-21C IR LED, which turns on and off using a 10-kHz oscillator frequency. By varying the LED's current, you control the level of transmitted power and, hence, the detection range. To save power, the transmitting pulses have a typical duty cycle of only 10%.
 |
||
| Figure 2. | An IR transceiver detects the presence of an object and provides an approximate distance from the transceiver. | |
The receiver circuit demodulates and amplifies the IR signals that the Everlight PD15-22C photodiode detects; the photodiode's peak sensitivity occurs at 940 nm. The photodiode output ac couples to the op amp's noninverting input. This coupling allows the 10-kHz signal to pass, but the coupling capacitor sets a 300-Hz cutoff frequency that prevents dc noise and background IR from reaching the amplifier.
Low noise, high bandwidth, and rail-to-rail-I/O capability make the op amp a good choice for demodulation and amplification in this circuit. In addition, its RF immunity prevents the annoying 217-Hz audio buzz that you commonly find in GSM (global-system-for-mobile)-communications cell phones. For the IR receiver, the op amp acts as a gain-of-100, second-order bandpass filter with a center frequency of 10 kHz. Thus, the op amp amplifies the incoming IR signals and demodulates them with a bandpass filter.
With no input IR signal present, the op amp is biased at 2.5 V. With a 10-kHz IR signal incident, its output varies around 2.5 V with a dynamic range of 5 V. The output drives a simple diode detector, which rectifies the 10-kHz signal and provides a dc signal proportional to its amplitude. This analog-output signal is proportional to the distance of the object from the IR transmitter. You can use it as is or feed it to an ADC for further processing.
 |
||
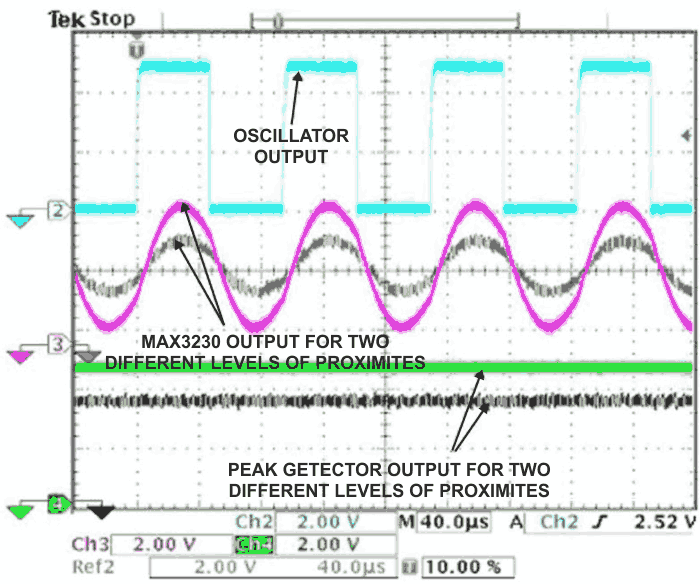
| Figure 3. | Different distances produce received waveforms of different amplitudes. | |
Figure 3 shows circuit operation at three nodes for objects at 1.2 and 1.4 in. from the IR transceiver. The circled numbers in Figure 2 refer to the oscilloscope traces in Figure 3.