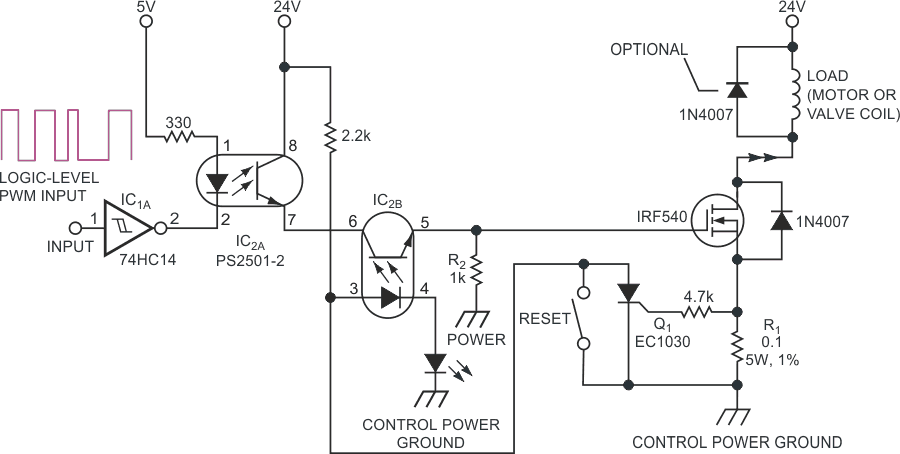
The circuit in Figure 1 allows standard TTL logic levels to safely drive a high-power dc load. The circuit provides for both signal and ground isolation as well as a solid-state circuit breaker.
 |
|
| Figure 1. | An overcurrent condition in this isolated PWM driver turns on SCR Q1, which stops IC2B from conducting. |
The input signal drives IC1A, which in turn provides drive current for optoisolator IC2A. In the absence of an overcurrent condition, IC2B conducts the signal to the gate of the MOSFET. When sufficient current passes through current-sense resistor, R1, to cause a voltage drop of approximately 0.7 V, SCR Q1 latches on. When Q1 is on, the circuit pulls Pin 3 of IC2B low, which stops the transistor side of IC2B from conducting. R2 then holds the gate of the MOSFET low, which prevents it from conducting until you reset the SCR.