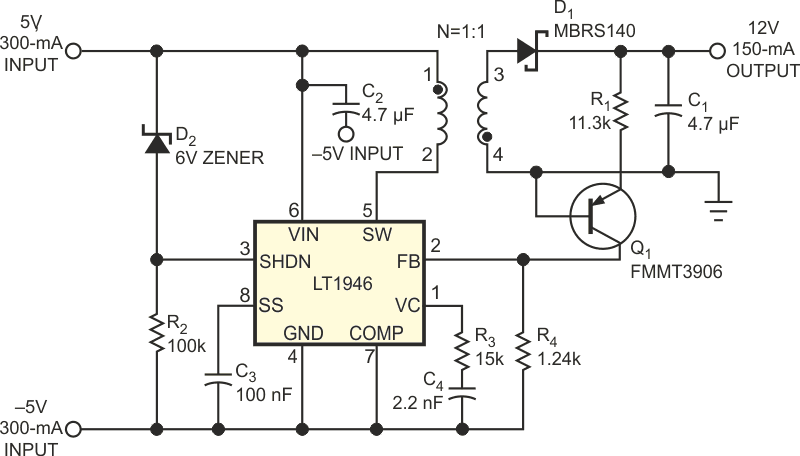
The schematic in Figure 1 shows a way to increase the power available from a current-limited 5 V supply by adding power from a –5 V supply. The dc/dc converter generates a single 12 V, 150-mA (1.8 W) output from two regulated and current-limited input sources at 5 V, 300 mA (1.5 W) and –5 V, 300 mA (1.5 W). Because the input uses different-polarity voltage sources, the design uses a flyback dc/dc converter to avoid a system-grounding problem. Level-shifted feedback sensing using a pnp transistor, Q1, references the feedback signal to the negative input voltage. You calculate the feedback-resistor divider by using the formula
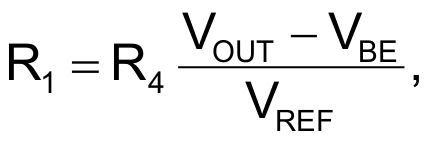
where R1 connects to the emitter of Q1, R4 connects to the collector of Q1, VBE is the base-emitter voltage of Q1, and VREF is the feedback reference voltage of the switching regulator.
 |
|
| Figure 1. | Combining two opposite-polarity power supplies can increase the available power from a flyback regulator. |
To simplify the circuit, the flyback converter in Figure 1 uses an LT1946 monolithic switching regulator. The voltage rating of the monolithic regulator has to be greater than the maximum switching voltage of the flyback converter, calculated by
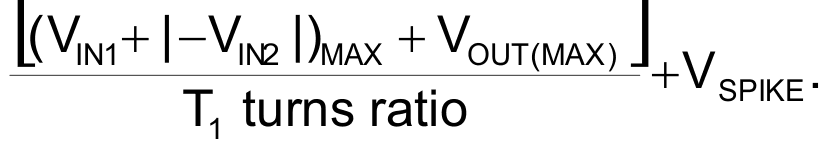
The maximum switching voltage is approximately 25 V for the circuit in Figure 1. Note also that the input capacitor and dc/dc regulator input must be able to handle a maximum input voltage of 10 V, resulting from the calculation +VIN1(MAX) + |–VIN2(MAX)|. In an event of fault-current conditions, such as shorted input or output, a zener diode, D2, creates the undervoltage-lockout threshold to turn off the LT1946 whenever either input source is in current limit or the input voltage (+VIN1 + |–VIN2|) drops below 6 V to help the input supply recover when the fault condition is removed. In a system with two available current-limited power supplies, you can convert the two supplies into a single supply that has more power-handling capability than either of the two inputs. A flyback topology based on an LT1946 monolithic converter offers a simple approach to the grounding problem and the feedback-sensing problem inherent in a dual-input power supply. Sharing the power between two input sources not only adds output-power capability, but also increases the overall flexibility of the system.
