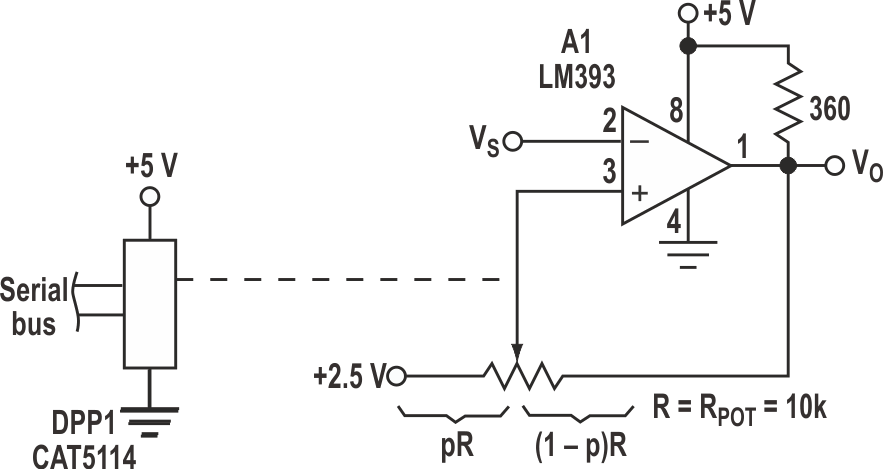
The circuit in Figure 1 is a single-supply version of a programmable Schmitt trigger, or a comparator with hysteresis. A comparator, A1, and a digitally programmable potentiometer (DPP1) are used for the function. The lower (VLL) and upper (VUL) limits of the hysteresis characteristic are a function of the relative setting of the potentiometer's wiper, given as:
VLL = (1 – p) · 2.5 V
and
VUL = 2.5 V + (p) · 2.5 V
where p is a dimensionless number from 0 to 1, representing the potentiometer wiper's position from one end of the pot (0) to the other end (1).
 |
|
| Figure 1. | A digitally programmable potentiometer enables adjustment to this Schmitt trigger’s upper and lower hysteresis limits, although the limits aren’t independently programmable. |
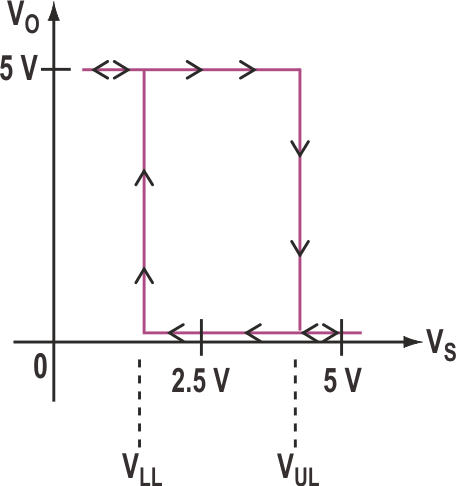
The characteristic's lower limit can be programmed from 0 to 2.5 V, while the upper limit can be programmed from 2.5 to 5 V. The circuit's transfer characteristic (VO versus VS) illustrates the hysteresis curve, and the lower and upper limits (Fig. 2). These limits are complementary, meaning that their values sum to 5 V. So, they're not in-dependently programmable.
 |
|
| Figure 2. | The transfer characteristic of the Figure 1 circuit illustrates the hysteresis curve, and the lower and upper limits. |
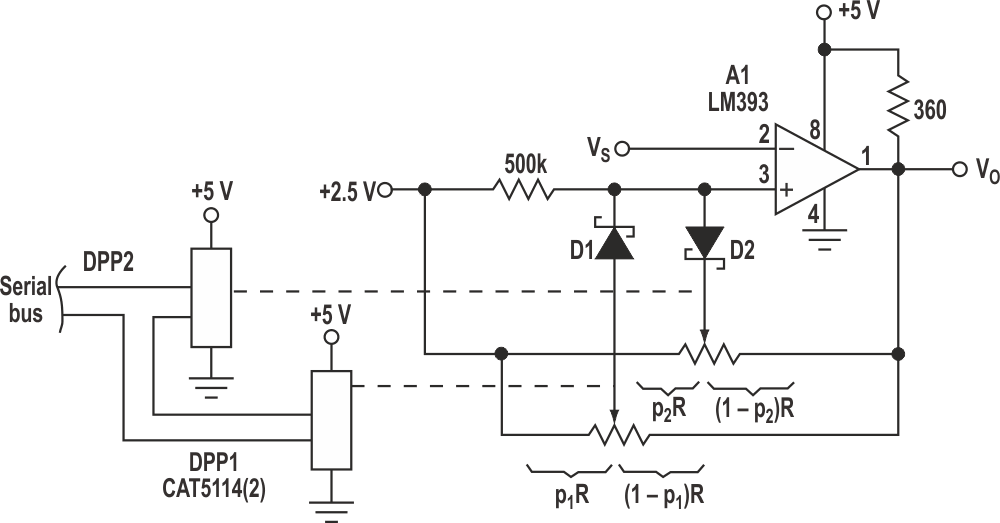
By adding steering diodes D1 and D2, plus a second potentiometer, the lower and upper limits of the characteristic can be independently programmed (Fig. 3). For this circuit:
VLL = (1 – p2) · 2.5 V
and
VUL = 2.5 V + (p1) · 2.5 V.
 |
|
| Figure 3. | Adding steering diodes D1 and D2, plus another potentiometer, allows independent programming of the upper and lower hysteresis limits. |
The CAT5114 32-tap DPPs let the lower limit be programmed from 0 to 2.5 V in 81-mV increments. The upper limit can be independently programmed from 2.5 to 5 V with the same resolution.