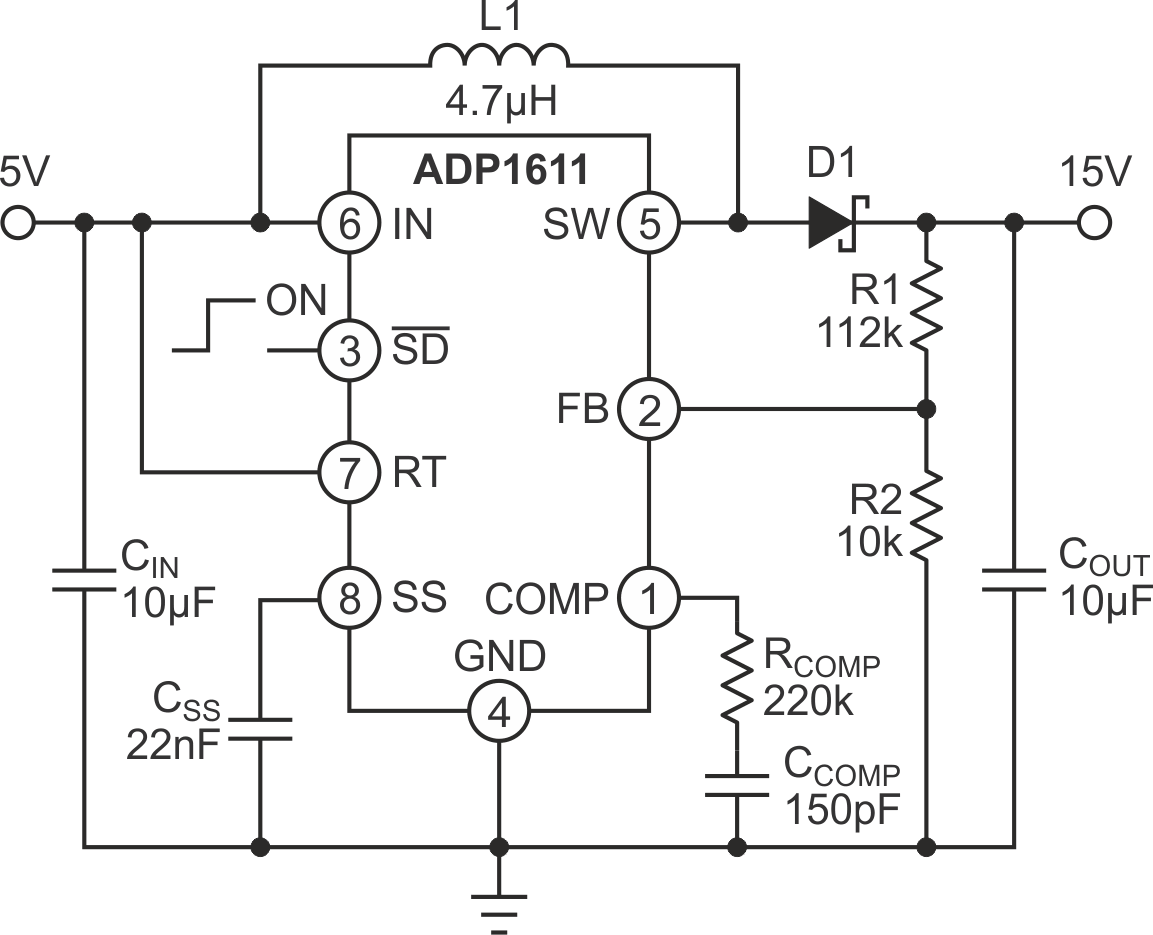
This is one real-life quest: How do we increase the output voltage of a step-up converter? If you have unlimited access to the right ICs, you are one lucky dog, but what if you don’t? Or maybe you are limited to a specific chip due to particular requirements, for instance, it is stable under some environmental conditions or, it has some specific features/interfaces or maybe, it’s easily accessible or cheap. Here, the ADP1611 step-up converter, is taken as an example. An application circuit can be seen in Figure 1.
 |
|
| Figure 1. | An application circuit for the 5 to 15 V ADP1611 step-up regulator. |
It has a 20-V limit on its output voltage; this limit is mainly due to the output switch of the ADP1611. Adding a tiny GaN FET such as the EPC2051 to the ADP1611 can increase this limit to above 100 V (Figure 2).
 |
|
| Figure 2. | A 5 V to 40 V step-up regulator with the addition of the GaN FET. |
The cascode, shown in Figure 2 consists of an internal switch transistor and the newcomer FET; it has better frequency characteristics than the internal switch alone. So, if the newly added GaN FET also has much lower on-resistance (RDS(ON)), then the internal switch, it will not reduce the efficiency.
To make the trick possible, the step-up converter should have an open drain (or open collector) output. Also, the connection of the inductor, diode, and the output of the chip must be reconfigured as shown in Figure 2. Diode D2 protects the internal switch from over-voltage.
Don’t forget to use this new value of the output voltage in your calculations. The output diode, capacitor, and inductor should also be rated to the new voltage. For the output diode, I used the HER107.
The addition of this GaN FET adds only 15 mΩ to the switch resistance of ADP1611 (0.23 Ω) – an increase of less than 10%. Please note, the gate-source voltage (VGS) of EPC2051 cannot exceed +6 V, so be careful.