The most common method for interfacing multiple switches – multiplexing – allows for the connection of (N/2)2 switches with N microcontroller I/O lines. The method described below, which has its roots in an LED interface technique commonly known as “Charlieplexing,” makes it possible to interface N×(N – 1) switches with N I/O lines.
In conventional multiplexing of an N-by-N matrix with 2N I/O lines, half of the lines are configured for input and half for output (at logic 0), permanently using a pin either for just the input or for just the output. The proposed method uses both states of an I/O pin, increasing the number of switches that can be interfaced to it.
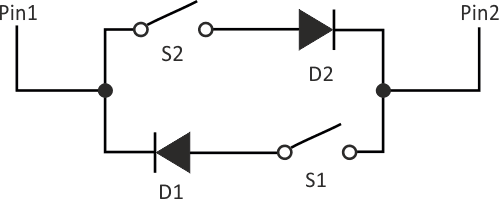
In the proposed method, every I/O pin is connected to every other pin with two switch-and-diode series circuits. Figure 1 shows a two-pin example. In this configuration, switch S1 can be read by configuring Pin2 to input mode and Pin1 to output mode (with logic 0). Switch S2 can be read by configuring Pin1 to input mode and Pin2 to output mode. This technique allows designers to interface six switches with only three pins, and a whole numeric keypad of 12 switches with four pins.
 |
|
| Figure 1. | Starting with this basic configuration, the improved switch interface technique can be scaled as needed. |
This configuration easily scales to any number of I/O pins, but between two I/O pins, the circuit essentially remains the same. For a circuit with N I/O lines, each I/O pin has N – 1 diodes leading in, and N – 1 diodes leading out. At any time, one pin is switched to logic 0, while the other N – 1 pins are configured in input mode for reading N – 1 switches attached to this pin. Generally, the N – 1 diodes leading into this pin can be replaced by a single diode, with all of the N – 1 switches connected to its anode.
 |
|
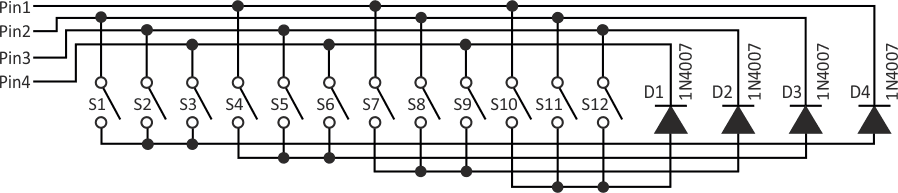
| Figure 2. | Extending the basic configuration, this circuit interfaces 12 switches using only four I/O pins of a microcontroller. |
Figure 2 shows a circuit for interfacing 12 switches using only four microcontroller I/O pins. To read switches S1-S3, Pin1 is set to logic 0, and Pin2, Pin3, and Pin4 are set to input mode. Similarly, to read switches S4-S6, S7-S9, and S10-S12, Pin2, Pin3, and Pin4 are, respectively, set to logic 0, while the rest are set to input mode.
 |
|
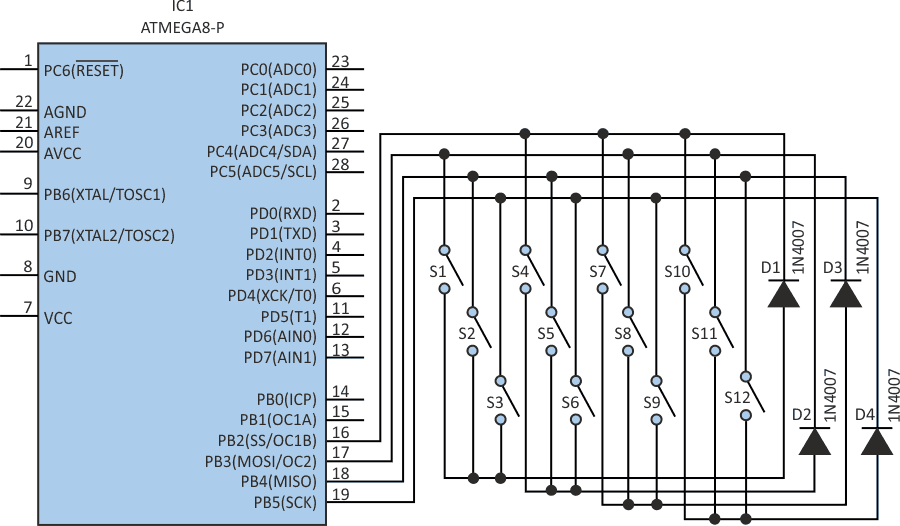
| Figure 3. | The 12-switch arrangement can be used to interface a numeric keypad to a microcontroller, in this case, an ATmega8. |
The circuit in Figure 3 demonstrates how a full numeric keypad interface can be connected to only four pins of a microcontroller (an Atmel ATMEGA8 in this case). The switches are pushbutton types, and the diodes are generic rectifying diodes. The demonstration program, written in C using WinAVR, successively sets one of the I/O pins to 0, and the rest to input, and it sets the state of the switches, which was relayed serially in mode 9600-8-N-1.
